Hydroelectricity is a renewable energy generation method that utilizes the power of water flow to generate electricity. The core equipment in a hydroelectric system is the water turbine generator. A water turbine generator (also known as a hydroelectric generator) is a generator that uses a hydroelectric turbine as the prime mover to convert water energy into electrical energy. Hydro generators can be used not only in large hydroelectric power plants, such as dams and reservoirs, but also in smaller versions suitable for home and small business use. This blog will give you an overview of how a hydro generator works.
Structure of Water Turbine Generator
The diagram on the right shows the structure of a water turbine. Coming up, PowerHome will introduce you to its various components and what they do: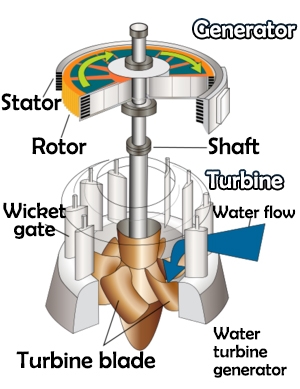
-
Rotor: The rotor is the core part of the hydro generator, which is mainly composed of the main shaft, impeller, magnetic poles and so on. The impeller is responsible for transferring the kinetic energy of water flow to the main shaft, while the magnetic poles generate the rotating magnetic field.
-
Stator: The stator is another important part of the hydro generator, which is mainly composed of iron core, coils, insulating materials and so on. The stator coil generates a fixed magnetic field, which interacts with the rotor poles to generate electromagnetic force.
-
Shaft: The shaft is the key component that supports the rotation of the rotor and is mainly responsible for bearing the weight of the rotor and ensuring the smooth rotation of the rotor.
-
Blades: Their main function is to convert the kinetic energy of the water flow into the kinetic energy on the blades, drive the turbine to rotate, and thus drive the generator to generate electricity. The design and arrangement of the blades directly affect the efficiency and performance of the turbine.
-
Wicket gate: The wicket gate controls the passage size of water flow by opening and closing, thus regulating the impact force and flow rate of water flow on the turbine blades, which in turn affects the rotational speed of the turbine and the output power.
Working Principle of Water Turbine Generator
The turbine is the central part of a hydroelectric generator and its structure is as described above. When water flows through the blades of the turbine, the kinetic energy of the water is transformed into dynamic force on the blades, which pushes the turbine to rotate, passing the energy to the shaft. The shaft is connected to the rotor of the generator and the mechanical energy is transferred to the generator. The generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by generating an induced current through the rotor in the presence of a magnetic field. The rotor rotates in the magnetic field to produce an alternating electric field, which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy through the principle of electromagnetic induction, and outputs usable alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC).
Simply put, a hydro generator uses the force of water to drive a turbine, which in turn drives a generator. If you want to experience its wonders without spending a dime, you can refer to How to DIY Hydroelectric Generator to make your own simple model.
Working Process
The operation of a water turbine generator is roughly divided into the following steps:

- Water flow guidance: Large hydroelectric generators are usually installed near rivers, dams or sluices with high water flows. The water flow is guided to the hydro generator by building facilities such as aqueducts and diversion pipes. While small domestic hydro generators can be driven by a tap water cage head, or some simple water diversion device.
- Water wheel rotation: water turbine generators are equipped with water wheels, i.e. wheels with blades. When the water flows through the water wheel, the current exerts force on the blades on the wheel, pushing the wheel to rotate.
- Rotation drive: The rotation of the water wheel is transmitted to the rotor of the generator through a transmission device (e.g., gears) to make it rotate.
- Generator operation: The wires in the rotor of the generator produce an electric current through changes in magnetic flux in the magnetic field. The relative motion between the rotor and stator of the generator produces an alternating magnetic field, which causes an induced electromotive force in the stator coils.
- Electrical output: The induced electromotive force is transmitted through the line to the electrical system and eventually supplied to the consumer.
Axial and Mixed-Flow Water Turbine Generators
Axial-flow turbines are the most common type of turbine. Its design principle is similar to that of aviation engines and ship propellers, and it utilizes the kinetic energy of the water flow to drive the water to rotate the rotor, so as to achieve the purpose of power generation. Its impeller is in the shape of a comb, parallel to the direction of the water flow, and the water enters the impeller and flows in an oblique direction, and then exits perpendicular to the direction of the rotor axis. Axial turbine has the advantages of simple structure, stable performance, high rotational speed, etc.
Design structure of mixed-flow turbine is between axial-flow turbine and radial-flow turbine. The impeller of mixed-flow turbine is axial-flow type in the upper part and radial-flow type in the lower part, and the water load area is near the outlet part. The water flow is compressed and bent along the blades, expanding again as it leaves the impeller and is in outflow.
The impeller design structure of these two types of generators is not the same, therefore, their working process will be slightly different. The impeller of axial-flow turbine is in the form of comb-like teeth, and the water flow enters parallel to the impeller, flows obliquely, and then exits perpendicular to the direction of the rotating axis. While the impeller of mixed-flow turbine is axial at the upper part and radial at the lower part, and expands again when it leaves the impeller and is in outflow condition. If you have a high flow water source and a low to medium head power plant, you can select this 5kW Axial-flow Water Turbine Generator, or if you want to power a vertical hydroelectric power plant with a high flow rate and head, the 10kW Mix-flow Water Turbine Generator will be the right choice.

This is all about the working principle of hydro generator. If you're interested in building an off-grid green home with a water turbine generator, or any other clean energy generator, welcome to powerhome.com, where you'll find great products at great prices and great blog content.
In conclusion, as a renewable energy utilization device, hydro generator has the advantages of simple structure, stable operation and high reliability. With the continuous development and utilization of hydraulic resources, water turbine generators play an increasingly important role in the power system. In the future development, water turbine generators will continue to optimize the structure, improve efficiency, and make greater contributions to the world's energy security and sustainable development.
(1).png)
(1).png)