After installing a solar panel system, it can be confusing when you see your electric bill. Some of the numbers and terms may seem illegible, but we're here to assure you that it's not that bad. By understanding the various components of your electric bill and how excess solar power plays a role in your bill, you can get a clearer picture of your energy usage and savings. This article will break down your electric bill in detail and explain how you can maximize your energy savings by interfacing the electricity generated by your solar panel system and how to work with the grid.
How Utilities Charge You for Grid Energy
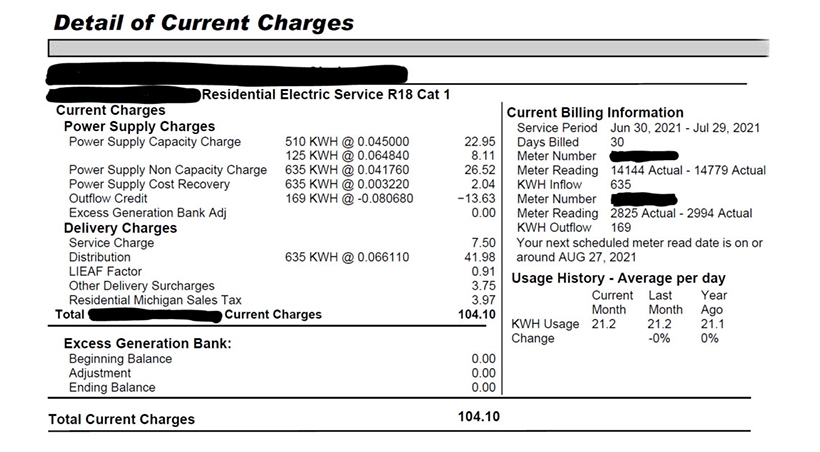
While everyone's electric bill is different, let's use the example of a customer in southeastern Michigan. The utility company charges you for each kilowatt-hour of electricity consumed in your home each month. Most utilities refer to this consumption as "inflow," which is the amount of electricity that flows into your home from the grid. You can find this term in the Current Billing Information section of your bill. This customer used 635 kWh of grid energy in July.
One of the biggest benefits of solar energy & solar panels is that some of the electricity generated can be sent back to the grid. This is called "outflow" on your statement, which is the amount of energy you send to the grid for the utility company to use. Depending on where you live and the utility company's policy, the amount of electricity you send back to the grid may be credited to your account at a 1-to-1 ratio. This means that for every kilowatt-hour of grid energy consumed by your residence, each kilowatt-hour of solar energy you send back to the grid has the same value, which gives you a significant benefit. This 1-to-1 excess energy credit is known as net metering.
How Do I Analyze My Electricity Bill?
In this customer's electricity bill, four charges are included: Supply capacity charge, supply non-capacity charge, supply cost recovery, and distribution charge. These fees total 15.6 cents per kWh consumed. Here are the specific cost components:
- Supply Capacity Fee: $0.045, or 4.5 cents
- Electricity Supply Non-Capacity Fee: $0.0417, or 4.2 cents when rounded to the nearest dollar
- Electricity Supply Cost Recovery: $0.0032, or 0.32 cents (one-third of a cent)
- Distribution Fee: $0.0661, or 6.6 cents (rounded up)
- Total: 15.6 cents/kWh
NOTE: The utility charges an additional fee for grid energy use above 510 kWh at a rate of $0.0648 or 6.5 cents rounded up.
Specific Impacts of Inflows and Outflows: For example, this customer pays at least 15.6 cents per kilowatt-hour of electricity he receives from the grid. Now let's look at the "outflow credit" portion of the statement. The customer sent 169 kWh of electricity to the grid and was credited $0.0806, or 8.1 cents per kWh (rounded up). Therefore, the electricity sent back to the grid is worth about half as much to them as the electricity used by the household.
What Do All the Terms on an Electricity Bill Mean?
As mentioned earlier, there are four main components of an electricity bill: The Supply Capacity Charge, the Supply Non-Capacity Charge, the Supply Cost Recovery, and the Distribution Charge.
- Supply Capacity Charge: The Supply Capacity Charge is the fee that the utility company charges you for generating electricity for your home. Of the 635 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity that this customer draws from the grid, the first 510 kWh are charged at a rate of 4.5 cents, and anything above that is charged at a higher rate, closer to 6.5 cents per kWh. These charges totaled $31.06.
- Supply Non-Capacity Charge: This customer was charged a Supply Non-Capacity Charge, which includes variable costs and operations and maintenance expenses. As with the Capacity Charge, the customer was also charged a usage fee of 635 kWh, totaling $26.52.
- Electricity Supply Cost Recovery Charge: The Electricity Supply Cost Recovery Charge is the least expensive of the four charges and covers fuel and associated power purchase and transportation costs from the power plant to the transmission system. Multiplying the 635 kWh of grid electricity they used by the rate of $0.0032, or $0.0032 (1/2), yields their total cost of $2.04.
- Distribution Cost: The distribution cost is delivering electricity through the grid to your home. The homeowner used 635 kWh and the cost of electricity was 6.6 cents per kWh, totaling $41.98.
Add all of these costs, as well as surcharges and taxes, and subtract your outflow credit, and you'll find that this electric bill is $104.10.
The Importance of Battery Storage Systems
Since some utility companies don't offer policies like net metering, it can be advantageous to use most, if not all, of the energy generated by your solar panels for your own home. If you send $1 worth of energy back to the grid and only get $0.50 back, it's not cost-effective. For this reason, we highly recommend that you purchase a battery storage system with basic knowledge along with your solar system. By storing excess solar energy in a battery backup, your home can utilize that energy for your needs instead of drawing energy from the grid. Batteries also protect you in the event of a power outage and allow you to deal with time-of-day rates, as some utility companies will charge you more for the energy you use at certain times of the day. Why not use your stored energy during these times to further increase the value of your batteries?
Knowing how to read your electric bill is essential to taking full advantage of your solar energy system. By having a clear understanding of the components of your electric bill and how excess solar energy is calculated, you can better manage your home's energy use and ensure that you are getting the most out of your energy savings. Installing a solar panel system not only reduces your energy costs, but also further improves your energy efficiency and reliability with a battery storage system.
We hope this tutorial on how to read your electric bill has been helpful. It's really about knowing how much electricity you use, how much you save, and finding out the net value between the two. Sign up for a free consultation with powerhome shop to learn more about how to optimize your solar system and your electric bill to ensure that you enjoy clean energy while maximizing your energy cost savings and achieving long-term economic and environmental benefits.
(1).png)
(1).png)