Solar Charge Controller
80A PWM Solar Charge Controller, 12V/24V/36V/48V
100A PWM Solar Charge Controller, 12V/24V/36V/48V
Solar charge controller is an automatic control device used in solar power generation system to control the charging of batteries by multiple solar cell arrays as well as the power supply from batteries to solar inverter loads. It provides and controls the charging and discharging conditions of the battery, and controls the power output of the solar cell module and the battery to the load in accordance with the power demand of the load, which is the core control part of the whole photovoltaic power supply system. Due to the different charging characteristics of various batteries, so the charge controller should be selected according to the type of battery. A wide range of solar charge controllers for sale at Power Home to suit your requirements.

Solar Charge Controller Function
In most photovoltaic systems, controllers are used to protect batteries from overcharging or overdischarging. Overcharging can cause electrolyte vaporization in the battery, leading to malfunctions, while overdischarging can result in premature battery failure. Both overcharging and overdischarging can potentially damage the load. Therefore, solar power charge controller is one of the core components of a photovoltaic power generation system and a major part of balancing the Balance of System (BOS).
In summary, the functions of a solar energy controller include:
- Power regulation function.
- Communication function: including simple indication functions and protocol communication functions such as RS485, Ethernet, wireless, etc., for backend management.
- Comprehensive protection functions: electrical protection against reverse connection, short circuit, overcurrent, etc.
Here is a detailed explanation of charge regulator functions:
- Overcharge protection: Automatically shuts off battery charging when charging voltage exceeds the protection voltage. The battery enters float charging mode when voltage drops to maintenance voltage, and float charging is deactivated when voltage falls below recovery voltage, entering equalization charging mode.
- Overdischarge protection: Automatically shuts off output when battery voltage falls below protection voltage to prevent battery damage. Output is automatically restored upon battery recharging.
- Overcurrent and short circuit protection for loads: Fuse wire melts if load current exceeds 10A or in case of a short circuit. Controller can be used again after fuse replacement.
- Overvoltage protection: Automatically shuts off output when voltage is too high to protect appliances from damage.
- Reverse charging prevention: Utilizes Schottky diode to prevent battery from charging solar panels.
- Lightning protection: Varistor prevents controller damage in the event of lightning strikes.
- Reverse connection protection for solar panels: Corrects polarity reversal for solar panel " + " and " - " terminals for continued use after correction.
- Reverse connection protection for batteries: Fuse wire melts in case of battery " + " and " - " polarity reversal. Controller can be used again after fuse replacement.
- Battery open circuit protection: If battery opens circuit, controller limits load voltage to prevent load damage during solar panel charging. No action is taken by the controller at night or when solar panels are not charging due to lack of power.
- Self-check: Allows controller self-check in case of natural factors or improper human operation, ensuring controller integrity and reducing unnecessary work time, thereby contributing to project quality and timeline.
- Recovery interval: Interval for recovery from overcharge or overdischarge protection to avoid load oscillation caused by line resistance or battery self-recovery characteristics.
- Temperature compensation: Monitors battery temperature and adjusts charging and discharging values accordingly to maintain battery operation in ideal conditions.
- Light control: Commonly used in automatic lighting systems, controller automatically switches off load output in sufficient brightness and switches it back on in darkness to achieve automatic control functionality.
Principle of Solar Charge Controller
Solar panels are photovoltaic devices (the main part is semiconductor material), which generate current through photoelectric effect after light irradiation. Due to the properties and limitations of the material and light, the generated current is also a fluctuating curve, if the generated current is directly charged into the battery or directly to the load power supply, it is easy to cause damage to the battery and the load, seriously reducing their life. Therefore, we must first send the current into the solar controller, using a series of special chip circuits to digitally regulate it, and add multi-level charging and discharging protection. When supplying power to the load, we also let the current from the battery flow into the solar controller first, and then send the current into the load after it is regulated. The purpose of doing so: one is to stabilize the discharge current; two is to ensure that the battery is not over-discharged; three is a series of monitoring and protection of the load and battery. If you want to use AC power equipment, you also need to add an inverter before the load to invert to AC.
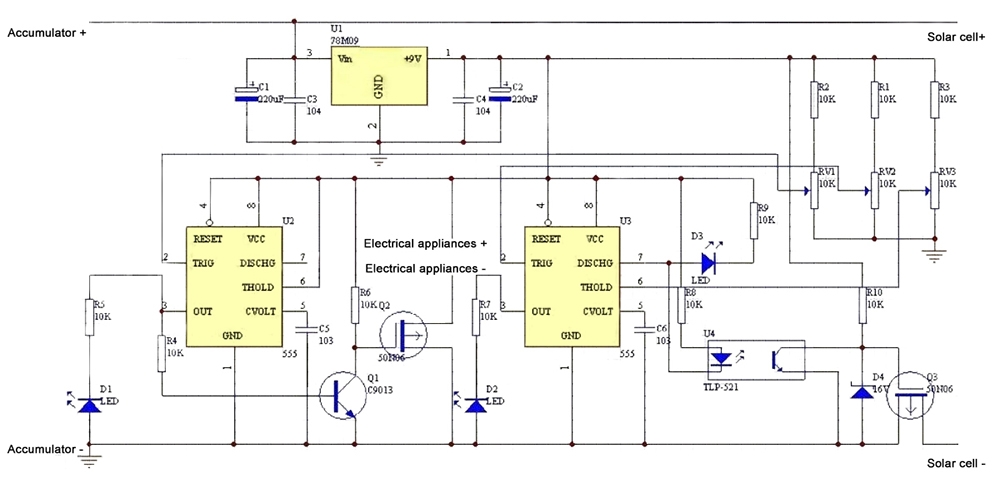
Solar Charge Controller Types
The popular solar controllers on the market are mainly ordinary solar controllers, PWM solar controllers and MPPT solar controllers.
Ordinary solar controller is the first generation of technology, the working principle is directly to the output of the solar panel hooked to the battery port, when the battery is sufficient to disconnect, because of the internal resistance of the battery, it is difficult to fill the battery, and the solar panel is not fully utilized, the charging conversion efficiency is only 70-76%, has been eliminated from the market, basically very few people use.
PWM solar controller is the second generation of technology, now the most on the market, the way of work is to use PWM control mode, relative to the ordinary solar controller, has improved a lot, can solve the problem of the battery is not full, charging conversion efficiency of 75 ~ 80%, but the solar panel is not fully utilized.
MPPT solar controller is the third generation technology, the most high-end solar controller, MPPT solar controller, refers to the "maximum power point tracking" (MaximumPowerPointTracking) function of the solar controller, is the PWM solar controller upgrade products. MPPT solar controller can detect the solar panel voltage and current in real time, and constantly track the maximum power (P=U*I), so that the system is always charging the battery with the maximum power, the MPPT tracking efficiency is 99%, the whole system power generation efficiency is as high as 97%, and the battery has an excellent management, which can be divided into the MPPT charging, constant voltage equalization charging, and constant voltage float charging. With the progress of technology and energy saving, the trend of MPPT solar controller replacing traditional PWM solar controller is irreversible.
Difference Between Solar Charge Controller and Inverter
Solar panels produce DC energy, and an inverter converts the DC power into AC power that can be used by household appliances and tools. A power inverter charger does the same thing, but it also converts DC to AC power to charge batteries. Hybrid inverters allow the grid, generators, and other types of AC power sources to charge batteries. Hybrid inverters like these can be used in grid-tied or off-grid solar systems. There are two basic types, pure sine wave and modified sine wave. Pure sine produces cleaner power but costs more.
The charge controller regulates the power going to the battery. Its task is to prevent overheating, overcharging and overloading. The charge controller also utilizes the power generated by the photovoltaic modules to charge the battery.
There are two types of charge controllers, PWM and MPPT.MPPT controllers do a more efficient job of optimizing solar energy and offer more configuration options.MPPT controllers are more expensive, but pulse width modulation is still the most widely used.
(1).png)











(1).png)