A wind turbine is a device that utilizes natural wind energy to convert it into electricity, which plays an important role in the renewable energy sector and can power your off-grid home with zero pollution. Do you know the types of wind turbines? This blog will introduce the two most common types of wind turbines - Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWTs) and Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs) - and describe in detail how they are different, and what the advantages and disadvantages of each are.
Overview of HAWTs & VAWTs
HAWTs have an axis that is horizontal, or parallel to the ground, which is the type of wind turbine one usually sees in wind farms. The head of the HAWT must be facing the wind for the rotor to rotate. There is usually a built-in yaw mechanism and wind vane used to automatically move the turbine in the direction of the wind. Horizontal axis wind turbines are the most commonly used type of wind turbine because they produce more electrical output than vertical systems, are more technologically advanced, and are more readily available in today's market.
VAWTs have an axis of rotation that is perpendicular to the ground. Because the axis of rotation is perpendicular to the ground, vertical-axis wind turbines are not limited by wind direction and can capture energy from the wind in all directions without relying on wind sensors or yaw systems to steer toward the wind. At the same time, VAWTs are quieter and suitable for urban use.
If you want to learn the basics about wind turbines, and the fundamental differences between HAWTs and VAWTs, please visit: What is a Wind Turbine?
Design
Currently, the momentum-blade element theory is commonly used for the blade design of HAWT, and the main methods are Glauert method, Wilson method, etc. However, the simplification inevitably causes the inaccuracy of the results because the blade element theory ignores the flow interference between the foliations, and the resistance of the airfoil is ignored when the foliation theory is applied to design the blade. This simplification has less effect on the blade shape design, but more effect on the wind energy efficiency of the wind rotor. At the same time, the interference between the blades of the rotor is very strong, and the whole flow is so complex that it is impossible to get accurate results if only relying on the blade element theory.
The blade design of VAWT used to follow the design method of horizontal axis and rely on the blade element theory. Because the flow of vertical axis wind rotor is more complicated than horizontal axis, it is a typical large separation non-constant flow, which is not suitable for analyzing and designing with the blade element theory, and this is one of the important reasons for the slow development of the manufacturing technology of VAWTs.
Generation Efficiency
The efficiency of HAWTs is affected by factors such as wind direction, blade design, and generator speed. In the case of constant wind direction, the higher the wind speed, the higher the efficiency, while the design of the blades directly affects the efficiency of wind utilization. Within a certain range, increasing the rotational speed of the generator can increase the generator efficiency. Overall, HAWTs can achieve relatively high generating efficiencies under the right conditions, often reaching more than 30%.
However, horizontal-axis turbines perform poorly in extreme wind conditions (lower roll-up wind speeds) and are typically shut down at high wind speeds to prevent damage to the turbine and its components.
VAWTs, on the other hand, have better directionality and are more adaptable to wind direction. Due to the difference in rotation, the rotor is subjected to an uneven distribution of wind, resulting in lower unit efficiencies, usually in the range of 10% to 20%. In addition, VAWTs result in higher costs due to the complexity of the model design and the difficulty of manufacturing.
They also have the unique advantage of being able to operate at high and extreme wind speeds, which is why vertical axis wind turbines are sometimes seen near mountains or cliffs.

Structural Features
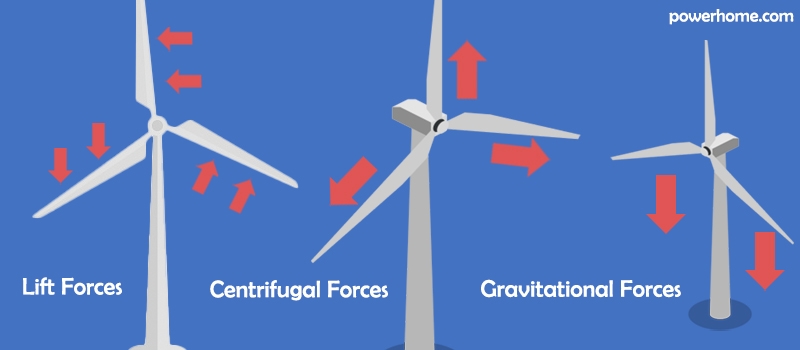
The blades of HAWT are subjected to a combination of inertial and gravitational forces during one week of rotation. The direction of the inertial force changes at any time, while the direction of the gravitational force is always constant, so the blades are subjected to an alternating load, which is very unfavorable to the fatigue strength of the blades. In addition, HAWTs are built higher in the air to withstand stronger winds, but maintenance of the machine and its components is not easy.
The blades of a VAWT are subjected to much better forces during rotation than those of a HAWT, and because the inertial forces are always in the same direction as gravity, they are subjected to constant loads and therefore have a longer fatigue life than horizontal axis wind rotors. They are built lower to the ground, which is a disadvantage because the closer to the ground the lower the wind speed; but it is also an advantage because the mechanical parts of VAWTs are easier to maintain.
Summary
Advantages of HAWTs:
- Higher Efficiency: The design of HAWTs allows them to be mounted higher, capturing more wind energy and generating more power in a smaller footprint. HAWTs generate electricity 20% to 40% more efficiently than VAWTs.
- Proven Technology: HAWTs are the most common type of wind turbine on the market, with proven technology and a wide range of applications.
- Cost-effective: HAWTs are very affordable compared to the expensive VAWTs, which is an advantage due to the maturity of the technology.
Advantages of VAWTs:
- Compact Size: Vertical axis wind turbines are compact and have a smaller overall shape, which allows them to better fit into complex urban environments or space-constrained locations.
- Insensitive to Wind Direction Changes: VAWTs do not need to be aligned with the wind, as they can capture wind energy from any direction.
- High Safety: Because the blades are close to the ground, VAWTs are safer to operate and easier to maintain.
Each type of wind turbine has its own advantages and disadvantages, please choose according to your needs. PowerHome offers you a wide range of high-quality wind turbines, as well as matching controllers and inverters.
In the future, wind power will become an increasingly important industry. Not only because it is a clean, renewable energy source, but also because it is already becoming more and more competitive in terms of operating costs and power generation efficiency. It is expected that with technological advances and policy support, the wind power industry will see greater development and application.
(1).png)
(1).png)