An inverter generator is a device that can control the output power and speed of a generator by adjusting the frequency. It can output constant frequency and voltage at different speeds and load conditions, and is widely used in industrial, commercial and household applications. PowerHome will bring you some basics of inverter generator to help users understand how it is categorized and how to realize the inverter function.

Working Principle of Inverter Generator
The basic structure of a portable inverter generator usually consists of a rotor and a stator, which is similar to the structure of an ordinary generator. The stator consists of the base, stator core, coil windings, and other structural parts that hold these parts in place. Rotor by the rotor core, rotor pole (magnetic yoke and pole coil), slip ring (also known as collector ring), fan and rotor shaft and other components. Through the bearing, seat and end cover will be the generator stator, rotor connection assembly, so that the rotor can rotate in the stator, through the slip ring through a certain excitation current, so that the stator becomes a rotating magnetic field, the stator coil to do cutting the magnetic line of force of the movement, thus generating the induced electromotive force, through the terminal leads, connected to the circuit, then the current is generated.
As the name suggests, the key to inverter generators is their use of an inverter to regulate the frequency and voltage of the output alternating current. This regulation allows the inverter generator to precisely adjust the output power parameters as required, especially in applications that require frequent adjustments to the output power, such as wind turbine power systems, where the use of an inverter generator can significantly improve the efficiency of energy utilization.
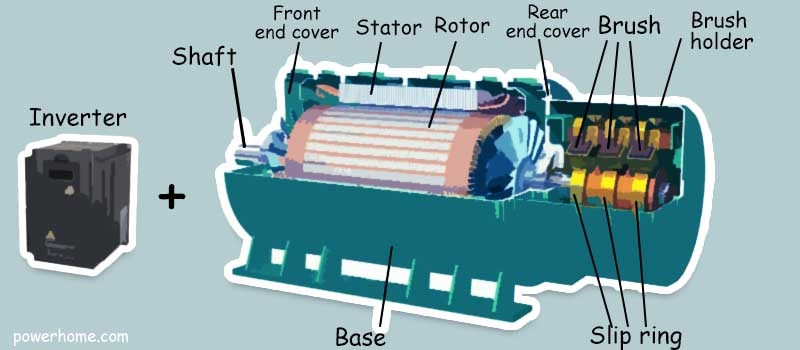
The basic principle of inverter generator is to control the power supply of generator by utilizing power electronic devices (e.g. thyristors, IGBTs, etc.), and regulate the output frequency and voltage by changing the rotational speed and load of generator. It adopts a number of advanced control strategies such as vector control technology, direct torque control technology, which can realize high-precision regulation of generator output power and speed. Compared with the traditional ordinary generator, the inverter generator realizes innovation and efficiency leap in energy conversion efficiency and output control.
In addition, the principle of operation of inverter generators involves the categorization of electrical energy, including alternating current (AC) generators and direct current (DC) generators. This indicates that inverter generators can handle not only AC, but also DC, which can be converted to variable frequency AC through inverters to meet the needs of different loads.
Classification of Inverter Generator
Classification by Control Mode
Inverter generator can be divided into open-loop control inverter generator and closed-loop control inverter generator and so on according to the different control methods. Open-loop control inverter generator adopts open-loop control system, the structure is simple, easy to operate, but the accuracy and control performance are inferior; closed-loop control inverter generator adopts closed-loop control system, with high accuracy, good control performance and other characteristics, but the structure is complex, more difficult to debug.
Classification by Fuel
Different types of inverter generators choose different fuels depending on their design, use and efficiency requirements. For example, small portable inverter generators (e.g., this 2000W portable inverter generator) usually use gasoline or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) as fuel, as gasoline generators are relatively lightweight and easy to carry and move. Large industrial inverter generators, on the other hand, often use diesel fuel or natural gas, especially for continuous operation or as the main power source.
In some countries or regions, kerosene may also be used as a fuel for inverter generators, especially in industrial applications where emission requirements are not particularly stringent. In regions where emissions are strictly regulated, new energy systems using photovoltaic panels and wind turbines to generate electricity are popular. Although solar energy systems cannot directly fuel inverter generators, they can be used in combination as a back-up energy source for each other.

Classification by Speed Regulation Mode
Frequency converter generators can be divided into:
- Constant frequency constant voltage inverter generator;
- Constant frequency variable voltage inverter generator;
- Variable voltage variable frequency inverter generator.
The first type of generator output frequency and voltage constant, applicable to the need to stabilize the frequency and voltage of the occasion; the second type of generator output frequency constant, while the voltage can be adjusted, applicable to the need to change the voltage but not change the frequency of the occasion; the third type of generator output voltage and frequency can be adjusted, applicable to the need to change the voltage and frequency at the same time of the occasion.
In short, the inverter generator is a very common new type of generator, which works on the principle of motor speed control through power inverter technology to realize the control of output voltage and frequency. It has a wide range of applications in many fields such as domestic, commercial, industrial, mining, agriculture and construction sites, helping people to supply energy for off-grid home as well as better use of electricity.
(1).png)
(1).png)