Off-grid inverters, as a core component of modern energy solutions, are gaining increasing attention. The role of off-grid inverters is to separate the solar power system from the grid, forming an independently operating microgrid system. During normal operation of a solar power system, the solar panels generate DC power, which is converted into AC power by a shunt inverter and injected into the grid. In this way, the solar power system can sell the excess electricity to the grid, thus realizing the feedback of electricity.
An off-grid inverter is a power conversion device that is primarily used to convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) for use in homes and other off-grid applications. In an off-grid solar system, the inverter plays a vital role in converting the DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power that can be used by household appliances.
How Off-Grid Inverters Work
An off-grid solar system typically consists of photovoltaic panels, an off-grid inverter, batteries, and a power management system. Solar panels collect sunlight during the day and convert it into DC electricity. This DC power can then be supplied directly to DC devices or converted to AC power through an off-grid inverter for use by AC powered devices. To ensure that power is still available when there is no sunlight, excess power is stored in batteries.
Off-grid inverters work on the principle of power electronics, where DC power is converted into AC power by means of an internal electronic circuit. This process usually involves a technique known as PWM (Pulse Width Modulation), which produces a near-sinusoidal current, making the inverter's output more suitable for the operation of household appliances.
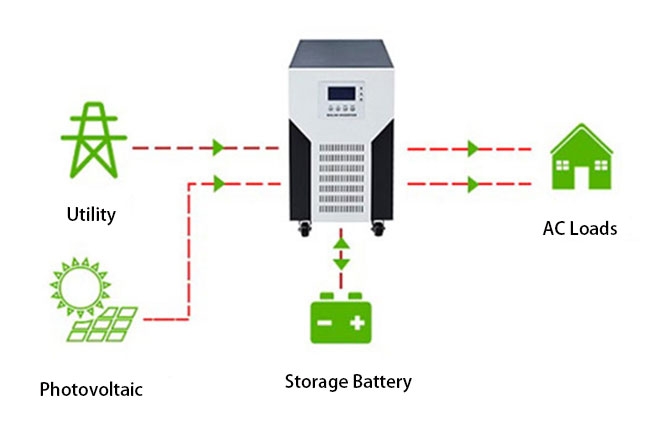
In off-grid living, the use of an off-grid inverter allows for a self-sufficient energy solution by taking the living area away from the conventional grid. This is especially important for residents in remote areas who may not be able to easily connect to a centralized grid. Additionally, off-grid solar systems reduce dependence on fossil fuels, which reduces environmental pollution and improves energy sustainability. PowerHome.com is selling a wide range of off-grid solar inverters that are designed for use in off-grid solar systems (PV Inverter Off Grid) to support homes in achieving off-grid living.
Inverter Display Showcase
The display screen of an off-grid inverter serves as a crucial interface for user interaction, enabling real-time monitoring and management of the inverter's operational status. The primary functionalities of the off-grid inverter display screen are outlined as follows:
- Operating Mode Display: The screen indicates the current operating mode of the inverter, such as inverter mode, charging mode, and bypass mode.
- Input and Output Parameter Monitoring: The screen provides real-time display of essential parameters, including input voltage, output voltage, and output power.
- Battery Status Monitoring: The screen offers detailed information on the battery status, including battery voltage, battery capacity, and the state of charge and discharge.
- Fault Alarm Display: When a fault occurs, the screen displays specific fault codes or types, assisting users in quickly identifying and addressing the issue.
- Historical Data Recording: Some high-end off-grid inverters feature a display screen with the capability to record historical data.
- User Settings Interface: The screen provides a convenient user settings interface, allowing users to adjust inverter parameters such as output voltage settings and charging current settings, thereby accommodating various application scenarios.
Classification of Inverters
According to the Nature of Wave Strings
There are two main categories, sine wave inverters and square wave inverters. Sine wave inverters produce sine wave alternating current (AC) that is as good as or better than the power grid we use every day because it is free from the electromagnetic pollution found in the power grid. Square wave inverters, on the other hand, output a poorer quality square wave AC, with positive maxima to negative maxima occurring almost simultaneously, thus causing dramatic instability to the load and the inverter itself. At the same time, its load capacity is poor, only 40~60% of the rated load, can not take inductive loads (see the following article for a detailed explanation). If the load is too large, the third harmonic component contained in the square wave current will increase the capacitive current flowing into the load, which will seriously damage the power filter capacitor of the load.
For the above shortcomings, in recent years, the quasi-sine wave (or modified sine wave, modified sine wave, analog sine wave, etc.) inverter, its output waveform from the positive maximum value to the negative maximum value of the interval between the use of the effect has been improved, but the quasi-sine waveform is still composed of folded lines, belongs to the category of square wave, the continuity of the bad. To summarize, sine wave inverters provide high quality AC power and are capable of driving any kind of load, but the technical requirements and costs are high. Quasi-sine wave inverters can meet most of our power needs with high efficiency, low noise and moderate price, thus becoming the mainstream products in the market. Square wave inverters are made by simple polytunnel oscillator, whose technology belongs to the level of 50's and will be gradually withdrawn from the market.

Inverters are categorized into coal power inverters, solar power inverters, wind power inverters, and nuclear power inverters depending on the power source. According to the different uses, it is divided into independent control inverters and grid-connected inverters. Efficiency of inverters in the domestic market. As mentioned above, the inverter itself consumes part of the power when it works, so its input power is greater than its output power. The efficiency of an inverter is the ratio of the output power of the inverter to the input power. If an inverter inputs 100 watts of DC power and outputs 90 watts of AC power, then its efficiency is 90%. When choosing an off grid solar inverter, it is important to consider its capacity, efficiency, compatibility, and whether it supports integration with batteries and other energy management systems.
According to the Nature of the Source Current
Active inverter: It is the inverter that makes the current in the current circuit, which is connected to the grid on the AC side and not directly to the load.
Passive Inverter: An inverter that makes the current in the current circuit, on the AC side, not connected to the grid but directly connected to the load (i.e., inverts the DC power to a certain frequency or adjustable frequency AC power to supply the load).
Off-Grid Inverters Related Terms
Inductive Load
Commonly known as high-power electrical products made by applying the principle of electromagnetic induction, such as motors, compressors, relays and so on. These products require a much higher starting current (about 5~7 times) than is needed to maintain normal operation. For example, a refrigerator that consumes about 150 watts of power during normal operation can have a starting power of more than 1,000 watts. In addition, due to inductive loads in the power supply or disconnect the power supply at the moment, will produce a reverse electromotive force voltage, the peak value of this voltage is far greater than the inverter can withstand the voltage value, it is easy to cause instantaneous overloading of the inverter, affecting the service life of the inverter. Therefore, these appliances have higher requirements on the power supply waveform.
Quasi-sinusoidal Waveforms
Quasi-sinusoidal waveforms are also divided into several types, ranging from square waveforms, which are not far from square waveforms, to rounded trapezoidal waveforms, which are closer to sinusoidal waveforms. We will only discuss square waveforms, which are the waveforms that most commercially available HF inverters can provide. These quasi-sinusoidal inverters can be used in laptop computers, televisions, stereos, camcorders, digital cameras, printers, various chargers, PDAs, game consoles, DVD players, mobile DVDs, home therapies and so on, and inverters with larger output power can also be used in small electric heating appliances such as hair dryers, electric cups, kitchen appliances and so on.
However, it is not suitable to use quasi-sinusoidal inverter for a long time to supply inductive loads such as refrigerators, electric drills, etc. Otherwise, it may cause damage to the inverter. Otherwise, it may cause damage to the inverter and related electrical products or shorten the expected service life. If inductive loads must be used, it is recommended to use quasi-sinusoidal inverters with larger reserve power, such as the large peak power inverters provided on this website. Here, an example of quasi-sinusoidal wave inverter applied to a television set (traditional monitor type) is highlighted.

Televisions have the following three requirements for inverters
- First: When the TV is turned on, the degaussing circuit has a great instantaneous demand for power, so the peak power requirement for the inverter is very high. For example, a 25-inch digital color TV consumes about 80 watts of power under normal operating conditions, while the instantaneous power at power-on is as high as 1,450 watts.
- Second: because the field frequency of the TV is equal to the AC grid frequency, the frequency of the AC output from the inverter must be accurate. Third, the inverter should not interfere with the TV set. Even if the above three conditions can be met, when the TV set is using quasi-sinusoidal AC power, there will still be a few fixed interference lines on the screen, and the color will be slightly greenish (when using an old TV set, the color deviation is more serious), but nothing else is different.
- Third: Some electrical appliances or tools that use electric motors, such as refrigerators, washing machines, drills, etc., require a large amount of current to propel them at the moment of startup, and once they are started successfully, only a smaller amount of current is needed to maintain their normal operation. Therefore, for inverters, there is also the concept of continuous output power and peak output power. The continuous output power is the rated output power; the peak output power is generally two times the rated output power. It must be emphasized that some electrical appliances, such as air conditioners, refrigerators and other start-up current equivalent to 3-7 times the normal operating current. Therefore, only inverters that can meet the peak starting power of electrical appliances can work properly.
An off-grid inverter is the core component of an off-grid solar system, designed for homes that wish to live and work off-grid. This inverter converts the DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power that can be used for household appliances. Unlike grid-tied inverters, off-grid inverters are not dependent on the public power grid, allowing homes to operate independently in areas not served by the grid.
At PowerHome, consumers can find a wide range of high-quality off-grid solar inverters (also known as PV inverters off-grid) designed for homes that want to harvest energy from the sun and become energy self-sufficient. These devices not only increase energy autonomy, but also reduce dependence on fossil fuels and help protect the environment.
When choosing the right off-grid inverter for your home, several factors should be considered, such as power requirements, energy efficiency ratio, and cost.The off-grid inverters offered by PowerHome.com are designed to meet the needs of a wide range of households, whether they're small or large and require high energy output. Off-grid inverters offer the possibility of realizing the dream of families seeking a self-sufficient lifestyle. By choosing the right inverter, whether it is an off-grid solar inverter or a solar inverter suitable for both off-grid and grid-connected applications, families can enjoy a reliable, economical and environmentally friendly energy supply and move towards a greener, more sustainable future.
(1).png)
(1).png)