Photovoltaic panels collect solar energy and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. However, most homes and businesses use alternating current (AC). Inverters, which convert the DC power from the PV panels into usable AC power, are an integral part of solar power systems. By function, solar inverters can be categorized into off-grid inverters and on-grid inverters. Well, what is the difference between them? This blog will tell you all about it.
Definition
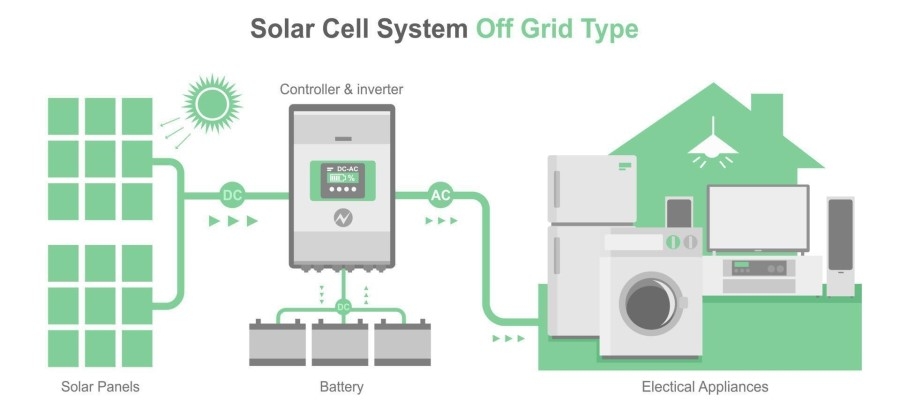
Off-grid solar inverter is a device that can convert the DC power generated by solar panels into stable AC power for charging and powering off-grid loads and batteries. It has the ability to supply power independently and is suitable for scenarios far away from the grid, such as suburban areas, mountainous regions, camping in the wild, and so on.
In contrast, on-grid solar inverter, also known as grid-tied inverter, is used to convert the DC power generated by solar panels into AC power, which is directly connected to the grid to supply power for domestic, industrial or commercial needs. The on-grid inverter does not have the ability to supply power offline, so in case of a grid outage, it will automatically disconnect the power to ensure the safety of the grid.
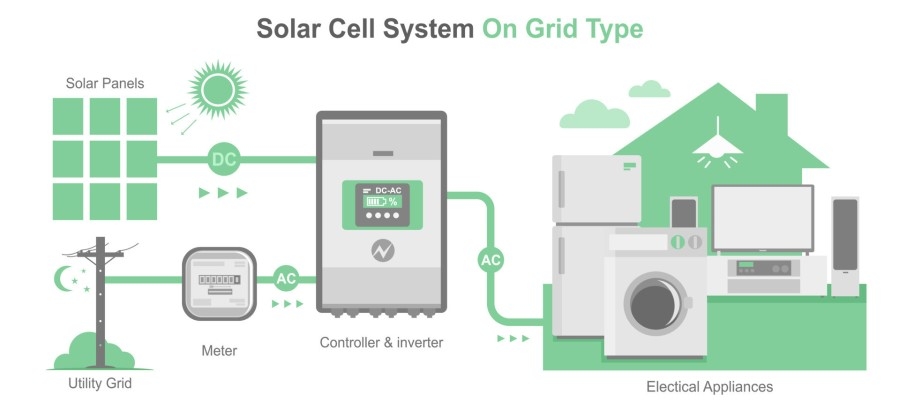
As you can see, the biggest difference between an off-grid inverter and on-grid inverter is whether it needs to be connected to the grid or not. Off-grid inverter is a system that is detached from the public power grid, and it can directly connect the converted AC power to the load for use or store it in the battery; on-grid inverter doesn't do any battery storage, and sends the AC power directly to the public power system.
Performance Comparisons
- Efficiency: Modern on-grid inverters are typically highly efficient, with some models achieving conversion efficiencies in excess of 98%. In contrast, the conversion efficiency of off-grid inverters is relatively low, but also depends on the specific application and design; moreover, off-grid inverters store the converted energy in the battery, which also causes some energy loss during battery charging and discharging.
- Stability: Off-grid inverters operate completely independently from grid fluctuations and have better output waveform quality, which is suitable for occasions with higher requirements on voltage fluctuations. On-grid inverters need to run synchronously with the grid and are easily affected by grid interruptions, while the quality of the output waveforms is poorer, which is not as good as off-grid inverters in terms of stability. However, off-grid systems usually require more maintenance, especially for the batteries.
- Cost: Grid-inverters are more complex and expensive due to the need to consider issues such as synchronization with the grid and frequency matching. In contrast, off-grid inverters are simpler in principle and cheaper.
Application Scenarios
According to their own characteristics, off-grid inverters and on-grid inverters are usually active in different scenarios:
- Off-grid inverter: It is mainly applied in remote areas such as rural villages, islands, deserts, or used in small units such as households to provide users with a stable power supply. It helps to solve the problems of insufficient grid coverage and unstable power supply, and is suitable for emergency use.
- On-grid inverter: Mainly used in large-scale photovoltaic power stations, wind power plants and other occasions, it can directly connect the power generated by renewable energy sources to the power grid and supply it to users. It helps to improve the utilization rate of renewable energy and reduce energy waste.

How to Choose?
Both grid-tied and off-grid inverters offer unique benefits. Your choice will depend on your specific needs, location and budget.
Location
- If you are in an area with a stable public grid and you want to sell excess solar power to the grid, you need an on-grid inverter.
- If you are in a remote area or if the local grid is unstable, choosing an off-grid inverter will make sense.
Budget
- Grid-tied systems cost more to purchase. However, by sending excess power to the grid, users can receive a discount or subsidy on their electricity bill, thus realizing a return on their investment.
- Off-grid inverters are cheaper, although they do not receive these discounts because they do not involve the grid.
Power Requirements
- If your main goal is self-sufficiency or if your power needs are small, an off-grid inverter may be more suitable for you.
- If you need a lot of power, or want to feed solar power into the grid, then an on-grid inverter is a better choice.
With the continuous development of new energy technology and the expansion of application areas, inverter technology is also constantly innovating and improving. In the future, various types of inverters will better meet the needs of different scenarios and make greater contributions to the development of clean energy for mankind.
If you are interested in being able to utilize solar energy on the go while picnicking or camping, you can visit powerhome.com. We are an online store specializing in clean energy, not only off-grid inverters, but we also offer high quality portable solar generators, small solar panels and other equipment that we believe will help you live off-grid.
(1).png)
(1).png)